Class Patch#
Defined in File Patch.h
Class Documentation#
-
class Patch
Contains the information of a local mosquito population.
The population is divided into four types: juveniles (J), adult males (M), adult virgin (unmated) females (V) and adult mated females (F). These are then subdivided into six genotypes (in this order): WW, WD, DD, DR, WR and RR composed of a wild-type allele (W), a drive-type allele (D) and a resistant-type allele (R). Juveniles are also subdivided into age groups, ordered from oldest (0 days left to eclosion) to youngest (
max_dev- 1 days left), and do not have a specific sex. The population can carry out life-processes and interface with other classes to introduce gene drive mosquitoes into the Patch, carry out dispersal in and out of the Patch and aestivate.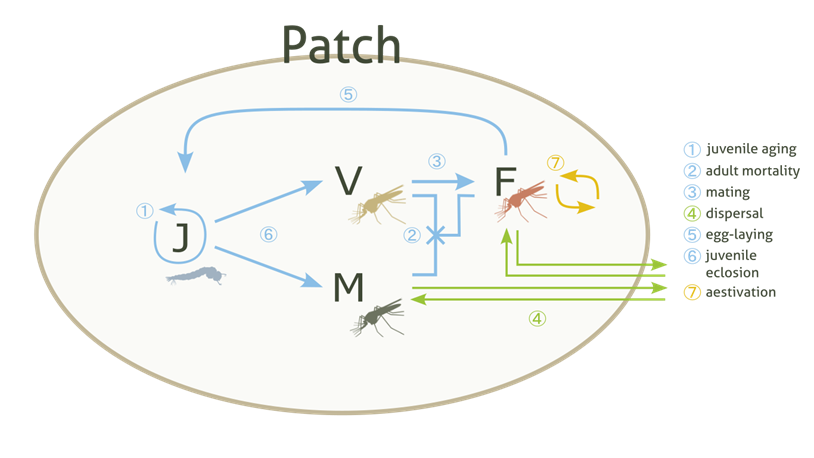
Public Functions
-
Patch(Model *mod, LifeParams *par, double a0, double side_x, double side_y)
Patch constructor for randomly generated coordinates.
Sets coordinates randomly on the square simulation space of size side x side.
Note
Coordinates range from 0 to side for bound checking purposes.
- Parameters:
mod – [in] Model pointer
par – [in] life parameters
a0 – [in] alpha0 carrying capacity baseline
side_x – [in] size of one side of the simulation area (x-axis)
side_y – [in] size of one side of the simulation area (y-axis)
-
Patch(Model *mod, LifeParams *par, double a0, Point point)
Patch constructor for custom coordinates.
- Parameters:
mod – [in] Model pointer
par – [in] life parameters
a0 – [in] alpha0 carrying capacity baseline
point – [in] patch coordinates
-
void populate(int initial_WJ, int initial_WM, int initial_WV, int initial_WF)
Populates the local site with a wild mosquito population.
- Parameters:
initial_WJ – [in] The number of initial wild juveniles.
initial_WM – [in] The number of initial wild adult males.
initial_WV – [in] The number of initial wild adult virgin (unmated) females.
initial_WF – [in] The number of initial wild adult mated females.
-
std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen> get_M() const
Returns the number of adult males in the patch, divided by genotype.
-
std::array<std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen> get_F() const
Returns the number of adult mated females in the patch, divided by female genotype and male sperm genotype.
-
std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen> get_F_fem_gen() const
Returns the number of adult mated females in the patch, divided only by female genotype.
-
long long int calculate_tot_J()
Calculates the total number of juveniles in the patch.
- Returns:
The total number of juveniles in the patch across all ages and genotypes.
-
long long int calculate_tot_M()
Calculates the total number of adult males in the patch.
- Returns:
The total number of adult males in the patch across all genotypes.
-
long long int calculate_tot_V()
Calculates the total number of adult virgin (unmated) females in the patch.
- Returns:
The total number of adult virgin (unmated) females in the patch across all genotypes.
-
long long int calculate_tot_F()
Calculates the total number of adult mated females in the patch.
- Returns:
The total number of adult mated females in the patch across all female and male sperm genotypes.
-
void juv_get_older()
Ages the juveniles of different age groups in the patch by a day.
The number of surviving individuals in an age group (for a given genotype) is determined by a binomial distibution of juvenile survival probability.
Note
Not all juveniles survive the aging process.
-
void adults_die()
Removes dying adults from the patch.
Determines the number of adults that die in the given day and removes them from the patch. The number of adult males that die (for a given genotype) is determined by a binomial distribution of adult mortality, and similarly for adult virgin and mated females.
See also
-
void virgins_mate()
Mates a fraction of the adult virgin females in the patch.
Determines the number of adult virgin females that mate in the given day (for a given female genotype) with a male of genotype j by using a binomial distribution of the mating rate. Then, tranforms the adult virgin females into adult mated females carrying male sperm of genotype j. Mating is carried out within the patch, and females only mate once.
-
void lay_eggs(const std::array<std::array<std::array<double, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen> &f, const std::array<double, constants::max_dev + 1> &dev_duration_probs)
Adult mated females lay eggs, creating new juveniles.
These juveniles do not have a specific sex.
Determines the number of eggs laid with genotype k on the given day by using a Poisson distribution. Other relevant parameters include the egg laying rate. Determines the development duration of these new juveniles using a multinomial distribution of development duration probabilities.
- Parameters:
inher_fraction – [in] inheritance fraction for new offspring
dev_duration_probs – [in] probabilities for juvenile development duration of new offspring
-
void juv_eclose()
Turns the oldest juveniles into adults.
The number of survivors is determined by a binomial distribution of the juvenile survival probability. The proportion of the individuals’ sexes upon eclosion is determined by a binomial distribution with 0.5 probability.
Note
Not all juveniles survive eclosion.
-
void update_comp()
Updates the juvenile survival probability of the patch.
Relevant parameters include the juvenile mortality rate, the juvenile survival probability power and the carrying capacity. The survival probability is computed as
\[ \textrm{comp} = (1 - \mu_j) \sqrt[\textrm{comp_power}]{\frac{\alpha}{\alpha + \textrm{J}_{\textrm{tot}}}}, \]with \( \mu_j \) juvenile mortality rate and \( \alpha \) carrying capacity.
-
void update_mate()
Updates the mating rate of the patch.
Relevant parameters include the beta parameter. The mating rate is computed as
\[ \textrm{mate_rate} = \frac{\textrm{M}_{\textrm{tot}}}{\beta + \textrm{M}_{\textrm{tot}}}. \]See also
-
void M_disperse_out(const std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen> &m_out)
Removes adult males from the patch as they disperse out.
- Parameters:
m_out – [in] The number of adult males dispersing out.
-
void F_disperse_out(const std::array<std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen> &f_out)
Removes adult mated females from the patch as they disperse out.
- Parameters:
f_out – [in] The number of adult mated females dispersing out.
-
void M_disperse_in(int gen, long long int m_in)
Introduces new adult males into the patch as they disperse in.
- Parameters:
gen – [in] The genotype index for the adult males to disperse into M.
m_in – [in] The number of adult males dispersing in for the given genotype.
-
void F_disperse_in(int f_gen, int m_gen, long long int f_disp)
Introduces new adult mated females into the patch as they disperse in.
- Parameters:
f_gen – [in] The female genotype index for the females to disperse into F.
m_gen – [in] The male sperm genotype index for the females to disperse into F.
f_disp – [in] The number of adult females dispersing in for the given genotype combination.
-
void F_hide(const std::array<std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen> &f_try)
Removes those females from the patch that attempt to go into aestivation.
- Parameters:
f_try – [in] The number of adult mated females that attempt to go into aestivation.
-
void F_wake(const std::array<std::array<long long int, constants::num_gen>, constants::num_gen> &f_wake)
Introduces back into the patch those females that wake up from aestivation.
- Parameters:
f_wake – [in] The number of adult mated females from the given patch that wake up from aestivation.
-
void add_driver_M(int num_driver_M)
Introduces driver heterozygous adult males into the patch.
- Parameters:
num_driver_M – [in] The number of driver heterozygous adult males to introduce.
-
Patch(Model *mod, LifeParams *par, double a0, double side_x, double side_y)